What is radiation?
The energy given off by matter in the form of high-speed particles or rays is called radiation.
To explain in detail, let’s talk about science. The matter is composed of atoms, which further have other parts, like the nucleus. The nucleus has minute particles called protons and neutrons. And the outer shell of the atom has electrons. The nucleus is positively charged, but the electrons carry a negative electric charge.
Atoms aim to attain a stable state, and this is done by giving off excess atomic energy. Unstable nuclei of an atom emit energy to attain stability. This spontaneous emission is what we call radiation.
Where can you find radiation?
Radiation is natural and is found everywhere. In our homes, offices, while commuting, or anywhere else on Earth. It is in the air we breathe. Natural radiation is also found in outer space. Radioactive elements are also present in our bones. And all these forms of radiation are harmless.
We are exposed to background radiation at all times. Most of this background radiation comes from naturally occurring elements. Like Uranium, for example. Some of it is cosmic radiation (radiation from outer space). And some from human-made sources. Human-made sources of radiation account for a very small part of background radiation. This is in the form of radioactive elements dispersed in the environment during nuclear testing or incidences like the one at Chernobyl in Ukraine.
Getting a CT scan, mammogram, and X-ray or traveling by flight also exposes you to radiation. An average human is exposed to 2 and 3 millisieverts (mSv) of radiation each year. However, the figure varies based on the exact location and lifestyle.
How can radiation be detected?
It is not possible to detect radiation using human senses. You cannot see, hear, smell, taste, or feel radiation. However, several instruments are available for detecting and measuring radiation.
The Geiger-Mueller (GM) tube, also called the Geiger counter, is the most commonly used radiation detection device.  A dosimeter is personal radiation detection equipment that is also popularly used.
A dosimeter is personal radiation detection equipment that is also popularly used.
Other devices include scintillation detectors, handheld survey meters, radiation portal monitor (RPM), and radiation isotope identification device (RIID).
What’s the difference between a Geiger counter and a personal radiation detector?
Named after Hans Geiger, a German scientist, the Geiger counter is a popular radiation detection equipment. It tells users about the presence of radiation near you. However, it cannot offer more details. A Geiger counter doesn’t show the source of radiation, its type, or even the amount of energy it contains.
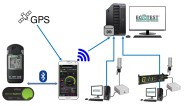
Unlike a Geiger counter, personal radiation detectors are wearable devices that tell you about the source, type, and intensity of radiation. They can also pinpoint the location from where radiation is coming. And thus, help the wearer take immediate action as per the situation.
Are there different personal radiation detectors for different purposes?
Yes, there are. Different situations require different types of devices. Like the EcotestCARD is best used by first responders to stay aware and alert about radiation. It also helps assess their history of radiation exposure.
Our Personal Dosimeter DKG-21M is a damp and dust-proof device. It aids those who need more robust and safe devices. You can visit here to know more about our personal radiation detection solutions suitable for different purposes.
Is there a noticeable difference between natural and artificial radiation?
No. There is no way you can differentiate between natural and artificial radiation.
Natural radiation that is omnipresent, called background radiation, sometimes also raises false alarms.
To avoid this, devices based on natural background rejection (NBR) techniques are used. With such devices, natural levels of background radiation get ignored. It gives alerts and warnings only when the radiation level exceeds the natural levels.
Why all this talk about radiation? Should I be scared of radiation?
Not at all. Radiation is not something to be scared of. It can save lives, and it is the natural way of life. However, when radiation is present in excess quantity (higher than ordinary radiation levels) and upon prolonged exposure, it causes several health-related repercussions.
First responders, certain medical professionals, and astronauts are at higher radiation risks. They need to be able to identify, detect, measure, and monitor radiation. Devices, like a dosimeter, make it possible.
Our aim behind this discussion about radiation is to spread awareness. We believe being aware is the first step towards being safe.
What is a ‘Dose’?
In reference to radiation, ‘dose’ refers to the energy of ionizing radiation that is absorbed per unit mass. This can be for any material.
Different types of doses mean different things, like –
Absorbed dose is used to assess the possibility of biochemical changes in certain tissues.
- Equivalent dose refers to the amount of expected biological damage due to the absorbed dose
- Effective dose measures the potential for long-term effects of radiation.
How will I know if I have been exposed to radiation?
If you have been exposed to high levels of radiation, you might experience radiation sickness. The official medical term is acute radiation syndrome. The symptoms include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Skin conditions like sunburns, sores, or blisters, and hair loss are possible. If you notice any of these symptoms, get medical help at the earliest.
If you have been exposed to lower levels (more than normal) of radiation, the symptoms might not show. Instead, you could suffer from cancer, cataract, or other issues later in life. Radiation detection and radiation monitoring devices can also let you know if you have been exposed to radiation. With such devices, you will also be able to ascertain the types of radiation, the level of exposure, and the source of radiation.
How do radiation detectors work?
Different types of radiation detectors – a personal radiation detector or non-personal detectors – work in different ways. There are three basic types of radiation detectors. And we have mentioned the principle behind their working below –
Scintillation detectors – Such devices make use of special materials that glow when exposed to radiation. Sodium-iodide, a type of salt, is the most common such material.
Gas-filled detectors – Such devices work when radiation passes through a specific gas used in the instrument. This causes the ionization of the molecules in the air. Then a high voltage is placed between two sections of the instrument. This causes positive ions to be attracted to the negative side of the detector (the cathode). The free electrons travel to the anode (the positive side). When collected by cathode and anode, a small amount of current is produced. A high-sensitivity current measuring device is then placed between the cathode and anode. When current is measured, which means radiation is present, a signal is displayed. The GM detector and ion chambers are types of gas-filled detector.
Solid-filled detectors – Such devices use semiconductors like silicon. These work in a manner very similar to ion chambers. However, solid-filled detectors are smaller in size and have a quick response time, making them much more suitable for first responders.